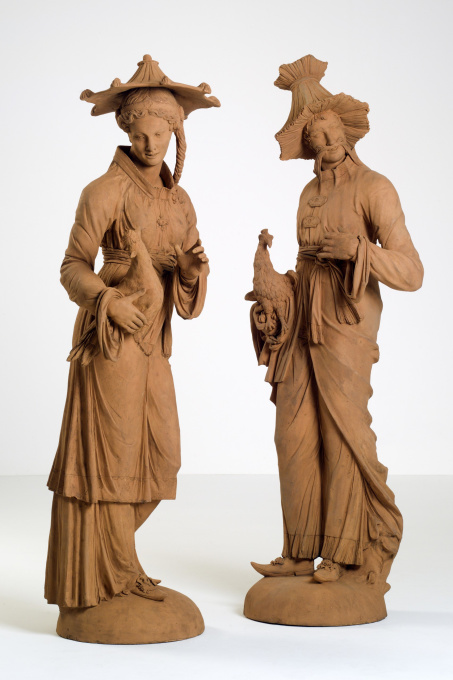
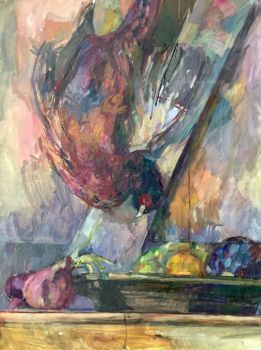Pair of German Terracotta Figural Sculptures Representing Two Malabars 1740 - 1760
Unbekannter Künstler
TerrakottaKeramik
130 cm
Derzeit nicht über Gallerease verfügbar
- Über KunstwerkA pair of terracotta figures smile at us. They are orientally dressed and are both carrying a bird. The attire is a European interpretation of what was thought to be Chinese (Japanese, Indian – in a word Oriental – ) clothing. The conical headgear and the moustache of the gentleman are most conspicuous, and it is for them that we, despite the European features, identify the pair as “Chinese”.
The birds that are carried by the two, are supposed to be the mythical Ho-Wo bird: a hybrid of pheasant, peacock and crane. This Japanese bird could be compared to the Chinese Feng or Fenghwang, the emblem of the Chinese empress. The Feng was, as one of the twelve ornaments, embroidered on imperial gowns and symbolised the shining example that the sovereign was supposed to be.
Chinoiserie
In 18th century Europe, many porcelain chinoiserie-figures were manufactured. Occasionnally these type of figures were also made of terracotta. In Germany these images were known as “Malebars”. They are chinoisery-statues named after the coast of Malabar (the west coast of India between Cochin in the south and Goa at the Arab sea). At the Malabar coast a number of trading posts were situated, that shipped exotic commodities like spices, fabrics, lacquerwork and porcelain out to Europe.
“Chinoiserie” is a typical European style. It is a very imaginative interpretation of what in Europe was thought to be the style of China. The lack of accurate information – Europeans were not allowed to enter China anymore after 1657 – forced the Europeans to go by the stories of Marco Polo, or the accounts of people like “Sir John Mandeville” who invented the stories of his travels through China himself. The prints from the hands of Joan Nieuhof that were made to account of the journey of the Dutch Mission from 1655-1657 to the Chinese Imperial Court, were of an equal influence on the image that Europeans generated on what they supposed to be China. Thus an idealised and romanticised China was created, where the emperor was a wise man and his ministers were all philosophers and the upper class lived in grand, magnificently furnished and decorated, houses.
The European “China-cult” reached its peak of elegance and frivolity in the 18th century, particularly under the influence of prints and paintings of Watteau and Boucher. Pavillions in Chinese style were build, Chinese gardens layed out and Chinese cabinets or parlours were fitted out. The Malebar couple were part of the interior of a Chinese cabinet of the period, more particularly the Chinese cabinet of schloss “Oranienbaum”, in Oranienbaum, a town east of Dessau in the German federal state of Sachsen-Anhalt.
Oranienbaum
The manor house of Oranienbaum was build between 1693 and 1702, commissioned by Henriette Catharina van Nassau (1637-1708). Her grandson Leopold III Frederik Frans van Anhalt Dessau (1740-1817) had the manor and the park adapted to the standards of the time in two stages. The first halls were build into Chinese rooms in 1766-1767 at the occasion of the marriage of the sovereign with Louise von Brandenburg-Schwedt (1750-1811).
In the great hall that gives on the park these two Malebars lived in two niches.
Fürst Frans was very much interested in science and art and was mainly occupied with the enlightment and archeology. He made educational excursions to Italy, France, the Netherlands, Switzerland and especially to Brittain. Frans was officially declared to be of age at october 20. 1758 and took on the reign of Anhalt-Dessau.
Frans is formostly known for the work he did on landscaping. He ended the regular floodings by constructing dykes, reinforcing dams and setting up the supervision over the waterways. His most famous project were the English Grounds of Wörlitz, also known as the Dessau-Wörlitz Garden Realm, one of the most important parks in Europe modelled after English style. Since november 2000 the Wörlitzer Park is on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Under Leopold III Frederik Frans the little princedom Anhalt-Dessau was moulded into a model-state of the German enlightment with a significant influence on Germany and the rest of Europe. He was succeeded by his grandson Leopold IV Frederik.
On his Grand Tour in England, Leopold III Frederik Frans van Anhalt Dessau was taken by the Chinoisery style that had become popular through William Chambers’ Designs of Chinese Buildings, Furniture, Dresses, Machines and Utensils that was published in 1757. Next to a copy of this work he also owned Plans, Elevations and Perspective Views of the Gardens and Buildings at Kew in Surry, that was published six years later. The park of Oranienbaum was formed into a Chinese water landscape by Fürst Frans. The original baroque island-garden was being redesigned following the ideas of Sir William Chambers between 1793 and 1797, resulting in the only (for the greater part) intact English English-Chinese garden of Germany today. The garden includes a five story pagoda, a water circumvented tea pavillion and several arched bridges.
Building history of Oranienbaum
The Oranienbaum palace was build in 1693, commissioned by Henriette Catharina van Nassau. In 1660 she had been given the village of Nischwitz, by her husband fürst Johan George II van Anhalt-Dessau, and named it into Oranienbaum as a reference to her descent. The palace was designed by the Dutch architect Cornelis Ryckwaert (1652-1693), a master of fortress-construction from the entourage of Johan Maurits van Nassau Siegen, governor of the city of Kleve. Johan Maurits lived in Brasil for a couple of years and was the first owner of the Mauritshuis in the Hague, hence its name. Cornelis Ryckwaert based his design on Dutch palaces like ‘t Loo in Apeldoorn and slot Zeist. Most probably he was an apprentice of Pieter Post who designed the Mauritshuis and Huis ten Bosch. The construction of the palace stalled with the architect's untimely death. The work was continued by the German Johan Tobias Schuchart. He completed the work of Ryckwaert and extended the palace between 1698 and 1702. Henriette lived at Oranienbaum until she deceased in 1708.
The interior
Some of the rooms were decorated with precious wallpaper, goldleather, tapestry and paintings from the Netherlands. As can be derived of an inventory of 1708 most of the furniture also was of Dutch origin.
The ground floor of the right wing is almost entirely taken up by the Teesaal with 17th century Dutch goldleather wallpapering that, to a large extent, still is intact.
The Teesaal was set up as a porcelain cabinet. The mantelpiece at the frontside and a niche at the opposite wall are fitted with brackets, that displayed precious porcelain. In the niche stood the piece de resistance of the collection; a table that was supported by dishes and vases, held together by brass fittings and a table top inlayed with blue and white Delftware tiles. The niche gave the impression of a porcelain cave. Most of the porcelain disappeared during and/or shortly after the second world war. The described table is now in schloss Mosigkau.
The sousterrain of the main building is typically decorated with Dutch blue and manganese coloured tiles. The blue tiles have biblical representations, the manganese tiles form five tableaus that have almost live-size depictions of the Roman gods Apollo, Mercurius, Mars, Luna and Venus. - Über Künstler
Es kann vorkommen, dass ein Künstler oder Hersteller unbekannt ist.
Bei einigen Werken ist nicht zu bestimmen, von wem sie hergestellt wurden, oder sie wurden von (einer Gruppe von) Handwerkern hergestellt. Beispiele sind Statuen aus der Antike, Möbel, Spiegel oder Signaturen, die nicht klar oder lesbar sind, aber auch einige Werke sind überhaupt nicht signiert.
Außerdem finden Sie folgende Beschreibung:
•"Zugeschrieben …." Ihrer Meinung nach wohl zumindest teilweise ein Werk des Künstlers
•„Atelier von ….“ oder „Werkstatt von“ Ihrer Meinung nach eine Arbeit, die im Atelier oder in der Werkstatt des Künstlers, möglicherweise unter seiner Aufsicht, ausgeführt wurde
•„Kreis von ….“ Ihrer Meinung nach ein Werk aus der Zeit des Künstlers, das seinen Einfluss zeigt, eng mit dem Künstler verbunden, aber nicht unbedingt sein Schüler
•"Art von …." oder „Anhänger von ….“ Ihrer Meinung nach eine Arbeit, die im Stil des Künstlers ausgeführt wurde, aber nicht unbedingt von einem Schüler; kann zeitgenössisch oder fast zeitgenössisch sein
•„Art von ….“ Ihrer Meinung nach ein Werk im Stil des Künstlers, aber späteren Datums
•"Nach …." Ihrer Meinung nach eine Kopie (jegliches Datums) eines Werks des Künstlers
• „Unterzeichnet …“, „Datiert …“. oder „Beschriftet“ Ihrer Meinung nach wurde das Werk vom Künstler signiert/datiert/beschriftet. Das Hinzufügen eines Fragezeichens weist auf einen Zweifel hin
• „Mit Unterschrift …“, „Mit Datum …“, „Mit Aufschrift ….“ oder „Trägt Unterschrift/Datum/Beschriftung“ ihrer Meinung nach die Unterschrift/Datum/Beschriftung von jemand anderem als dem Künstler hinzugefügt wurde
Artwork details
Related artworks
Unbekannter Künstler
Bvlgari Tubas Halskette1900
Preis auf AnfrageAns Hemke-Kuilboer Juwelier & Antiquair
1 - 4 / 12- 1 - 4 / 6
- 1 - 4 / 24
Carlo Bellini
A terracotta sculpture of a dodo20th century
Preis auf AnfrageZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 24Klaas II Mobach
Hanna Mobach, daughter of the sculptor Klaas Mobach, reading1950 - 1970
Preis auf AnfrageKunsthandel Pygmalion
1 - 4 / 24