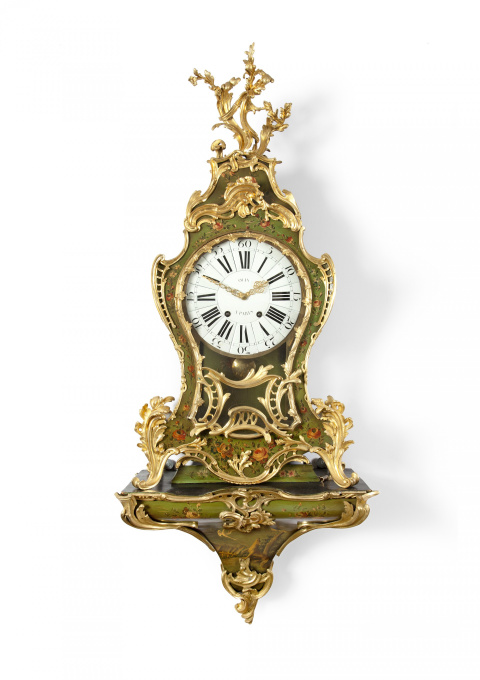
A Louis Quinze Console Clock 'Grand Cartel' late 18th
Jean-Charles Olin
BronzoOroMetalloSmaltoDorato
150 ⨯ 61 ⨯ 30 cm
Attualmente non disponibile tramite Gallerease
- A proposito di opere d'arteA LOUIS XV CONSOLE CLOCK ‘GRAND CARTEL’
signed on the dial ‘olin à paris’ | 3rd quarter 18th century | 150 x 61 x 30 cm
A Louis XV ormolu mounted vernis Martin console clock, ‘grand cartel’, signed on the white dial ‘olin à paris’. White enamel chapters surround the centre pierced ormolu hands. The case is decorated overall Vernis Martin with flowers and on the console is depicted a scene taken from ‘Fables de La Fontaine’, ‘Le coq et le renard’.
In French interior design, vernis Martin is a type of imitation lacquer named after the French brothers Guillaume and Etienne-Simon Martin. It imitated Chinese lacquer and European subjects and was applied to a wide variety of items, from furniture to coaches. It is said to have been made by heating oil and copal and then adding Venetian turpentine.
Jean-Charles Olin’s (d. after 1789) name is associated with a number of examples. Notably a Louis XV gilt bronze mounted Meissen porcelain pendule ‘à l’éléphant’ in the Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam and another clock housed at Schloss La Fasanerie, Fulda. Olin first worked as an ouvrier libre but was received as a maître-horloger in October 1776. He served as deputé of his guild later in 1777. Olin used some of the best Parisian case makers. They included the ébéniste Antoine Foullet, the ébéniste doreur Jean Goyer and the esteemed bronzier Jean-Joseph de Saint-Germain.
Jean de La Fontaine was a French poet and fabulist, who lived and worked during the 17th century. For special contributions to French literature he was elected to the French Academy of Sciences in 1684. Published in 1668, the collection of fables brought La Fontaine international fame. The works of the ancient Greeks, Indian storytellers, other fabulists and folk tales about animals serve as a source of inspiration for the author. Drawing motives from these works, La Fontaine brought new life to the fable genre. - A proposito di opere artistaJean-Charles Olin (morto dopo il 1789) è stato uno dei più importanti orologiai parigini della fine del XVIII secolo. Cognato dell'orologiaio Jean-Gabriel Imbert, lavorò inizialmente in modo indipendente, poi divenne maestro nel 1776 e aprì il proprio laboratorio nelle enclos des Quinze-Vingts. Con una reputazione in rapida crescita, nel 1777 fu eletto deputato della sua corporazione. Come i migliori orologiai del suo tempo, per le sue casse si affidava ai migliori bronzier, tra cui Antoine Foullet, Robert Osmond e Jean-Joseph de Saint-Germain. I suoi orologi furono acquistati da alcuni dei più importanti collezionisti del XVIII secolo. Gli orologi di Olin sono menzionati negli inventari di successione dell'avvocato Jacques-Augustin Auvray, de Marie-Philippe Donneau, marchese de Visé e la vedova del segretario del re Louis Paris de Treffonds.
Artwork details
Categoria
Soggetto
Stile
Materiale e Tecnica
Colore
Related artworks
Artista Sconosciuto
A Surinam-themed Amsterdam long-case clock1746 - 1756
Prezzo su richiestaZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 A cura di
A cura diGallerease Magazine
1 - 4 / 17Artista Sconosciuto
COPPIA DI TORCHÈRE O PORTACANDELE IN TEAK INDONESI LACCATI E DORATI18th century
Prezzo su richiestaZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
 A cura di
A cura diDanny Bree
Artista Sconosciuto
UN RARO GRANDE TELESCOPIO GIAPPONESE IN PELLE LACCATA1750 - 1800
Prezzo su richiestaZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Artista Sconosciuto
UN NETSUKE IN AVORIO DI UN OLANDESE CHE GIOCA CON UN RAGAZZINO18th century
Prezzo su richiestaZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Artista Sconosciuto
UN CONTENITORE PER DOCUMENTI DELLO SRI LANKA IN ARGENTO DORATO19th century
Prezzo su richiestaZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 24Gerard Bilders
The 'Uiterwaarden' at Oosterbeek (flood plains)1861
Prezzo su richiestaStudio 2000 Art Gallery
1 - 4 / 24- 1 - 4 / 24





















































































