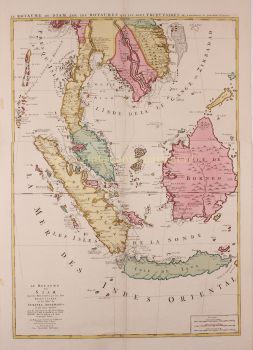
South East Asia 1630
Gerard Mercator
PapierAfdrukken
34 ⨯ 47 cm
€ 2.850
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De Jonge
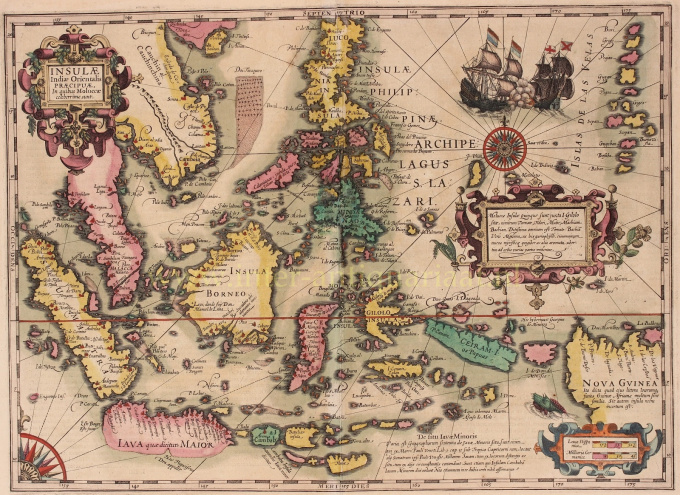
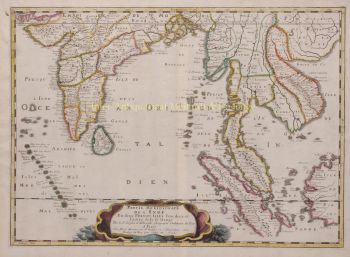
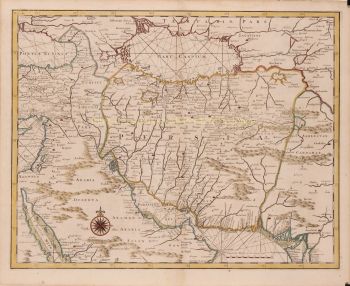
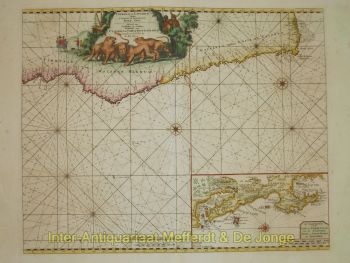
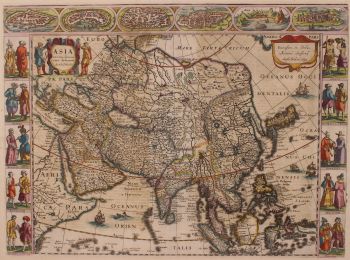
- Over kunstwerkDECORATIVE MAP OF THE EAST INDIES "Insulae Indiae Orientalis Praecipuae, In quibus Moluccae celeberrime sunt." Copper engraving made by Gerard Mercator published in Amsterdam in 1630 by Jodocus Hondius. Coloured by a later hand. Verso: Latin text. Size: 34,5 x 47,6 cm. Striking and highly decorative map of the East Indies from the Mercator-Hondius Atlas. It extends from the Philippines to Timor and Sumatra to New Guinea, detailing the Spice Islands, a region of great importance to seventeenth century Europe, but one about which little was known at the time. This map follows very shortly the extension of Dutch control over the islands. In 1602 the Dutch East India Company (VOC) was formed, and within a couple of decades the company came to control the region. The sandbanks and shoals around islands are marked, as are major settlements on the islands. A decorative text box in the sea east of the Philippines proclaims the rich spices available on the Moluccas Islands, including cinnamon, nutmeg, cloves, and ginger. In the lower right corner next to the scale, is a note about Java Minor, discussing the various locations chosen for the island by geographers. Java Minor was first mentioned in European literature in the Travels of Marco Polo. Polo identified Java Minor and Major; the first referred to the island of Sumatra (or Sumbawa) and the latter described Java as the largest island in the world. However, due to a scribal error in Book III of Polo's Travels, Java Minor was recorded as 1,300 miles south of Java Major. This caused confusion and debate on the part of geographers until the early eighteenth century with some using the name Java Minor (Petite Jave) for New Holland and others choosing it for Sumatra, Sumbawa, or Java. Marco Polo is not the only explorer mentioned on the map. Of particular note is the comment “Huc Franciscus Dra. Appulit”, which appears by the unknown southern coast of Java, representing Francis Drake's landing during his circumnavigation in 1577-80. Hondius knew of Drake's voyage first hand, as he was a religious refugee in London from 1583 to 1592 and an acquaintance of the navigator. Dutch and English ships are in the midst of battle shown on the map east of the Philippines. A visual representation of how hotly contested this area was in the early modern period. Another historical note is in the interior of Borneo, a cross marking one of the places traversed by the Portuguese Dom Manuel de Lima. Therewith revealing Hondius' Portuguese source, the portolan charts of Portuguese cartographer Bartolomeu Lasso. The Portuguese were some of the first Europeans to exploit the resources of the Spice Islands. They were joined by the Spanish, who were interested in stretching their empire from the eastern to the western Pacific. The Moluccas, as discussed in the text box on the map, were considered of particular value, as they were the world's only source at the time for nutmeg and cloves. Spain and Portugal eventually agreed to grant Portugal control of the Moluccas in the Treaty of Zaragoza in 1529, but the islands remained hotly contested for the next two centuries. By the early seventeenth century, the Dutch and English were jockeying for position in the region. In response to the Dutch Revolt, the Spanish King Philip II closed the Lisbon spice market to Dutch and English traders in 1585, spurring both countries to seek direct trade with Asia. The English East India Company was founded in 1600, followed in 1602 by the Dutch East India Company. More heavily capitalized than its English counterpart, the VOC aggressively moved into areas of Portuguese influence. This map reflects that Dutch influence at its impetus. Jodocus Hondius (1563-1612) was the founder of the famous 17th century Dutch map publishing family. Hondius, along with sons Jodocus II and Henricus and son-in-law Jan Jansson, was prominent in Dutch cartography and competed with the emerging Blaeu family map business. When Jodocus Hondius acquired the copperplates of the Mercator atlas, he prepared this map for inclusion in his “Atlas sive Cosmographicae”. Price: Euro 2.850,-
- Over kunstenaarGerard Mercator was born on March 5th,1512. He was a cartographer renowned for creating a world map based on a new projection which represented sailing courses of constant bearing as straight lines, an innovation that simplified navigation. In his own day he was the world's most famous geographer but in addition he had interests in theology, philosophy, history, mathematics and magnetism as well as being an accomplished engraver, calligrapher and maker of globes and scientific instruments.
Mercator wrote on geography, philosophy, chronology and theology. All of the wall maps were engraved with copious text on the region concerned. As an example the famous world map of 1569 is inscribed with over 5000 words in fifteen legends. The 1595 Atlas has about 120 pages of maps and illustrated title pages but a greater number of pages are devoted to his account of the creation of the universe and descriptions of all the countries portrayed. His table of chronology ran to some 400 pages fixing the dates (from the time of creation) of earthly dynasties, major political and military events, volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, and eclipses. He also wrote on the gospels and the old testament.
Mercator was a devout Christian born into a Catholic family at a time when Luther's Protestantism was gaining ground. He never declared himself as a Lutheran but he was clearly sympathetic and he was accused of heresy (Lutheranye). He spent six months in prison but he emerged unscathed. This period of persecution is probably the major factor in his move from catholic Louvain to a more tolerant Duisburg where he lived for the last thirty years of his life. Walter Ghim, Mercator's friend and first biographer, describes him as sober in his behaviour, yet cheerful and witty in company, and never more happy than in debate with other scholars, but above all he was pious and studious until his dying days
He died in 1594.
Bent u geïnteresseerd om dit kunstwerk te kopen?
Related artworks
- 1 - 4 / 24
Abraham Salm
Twenty-four chromolithographs of Java after A. Salm”1801 - 1876
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
A large wall map of Asia by Nicolas de Fer 1647 - 1720
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Onbekende Kunstenaar
A Dutch colonial Indonesian betel box with gold mounts1750 - 1800
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
Theo Meier
Een Balinese vrouw met offergaven1936
Prijs op aanvraagZebregs & Röell - Fine Art - Antiques
1 - 4 / 24- 1 - 4 / 24
- 1 - 4 / 12